AI Powered Personal Shopper: How Language Models are Revolutionising Customer Experience
(5 minute read)
- LLMs have revolutionised customer service by enabling automated, personalised interactions through natural language processing.
- Concerns exist around data privacy, potential bias in the models, and limitations in understanding complex, non-text-based customer needs.
- LLMs currently act as valuable support tools for customer service rather than complete replacements for human representatives

By William Willis and Yassa Ahmed
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has taken over the 2020s decade and has provided Large Language Models (LLMs) to assist in understanding and generating human-like text. The beauty of the LLMs revolution is how it inputs complex language patterns to output behaviours closely related to everyday speech; natural language processing (NLP).
This evolution of the human assistant has ushered in efficiencies beyond simply being able to write a clever essay or acknowledge differential equations. It has also crossed into the labour market, with its next generation customer service capabilities.
Predictive in diagnoses and personalised through a repository of information about you and the field you operate across, this is enabling continuous performance in different areas of the economy. Advancements in LLMs are positioning companies to adopt AI in customer service and day-to-day automation tasks.
Google Gemini, ChatGPT and Gronk are just tools enabling multiple language models into one interface within customer service. Intelligent chatbots are transforming consumer shopping, without another person behind the interface. Are these AI agents delivering greater responsiveness than one-to-one human interaction?
Traditional Means and The Customer Journey

Whether it be over the counter or on the phone, much of the relational aspect of product sale has been about how well, or exceptionally, the customer service is to land a deal. Prior to 2020, it was about how well you knew X person over Y to get you to purchase from their brand (for the point of this article).
The approach for businesses then, was to spend time to nurture and create a labour force well equipped to build rapport, objection handle and develop relationships. The well to do relationship manager, would understand risk and anticipate customer queries to nail the sale.
“The fact that you may meet resistance as soon as you try to establish contact”… “Nonetheless, anticipate resistance from the beginning” states Kimberly Richmond. Tried and true methods in utilising techniques was/is a good way to engage customers to help deliver on what they want.
Anecdotally speaking, the customer’s journey was powered by the competence of the human agent and the level at which they understood client need or, better yet, undiscovered needs for the client. If the customer ended up with an incompetent service representative, it led the potential buyer to be frustrated, unable to find the right product, have a personalised experience or be overloaded with information.
Business Applications of LMMs
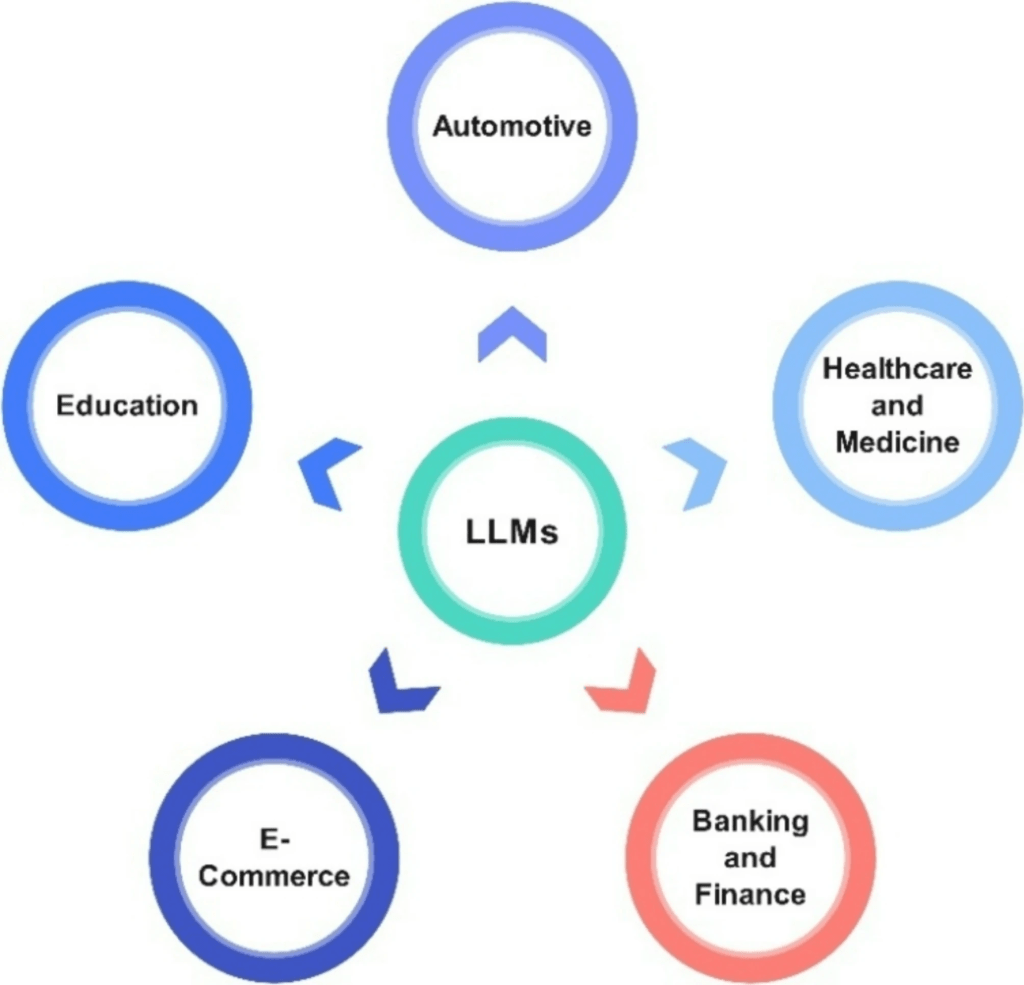
Traditional methods have suffered with inconsistency and the performance of their customer representatives, which can devalue a company’s offerings. In this respect, LLMs have widely been adopted to stem the unpredictability in client relations between differing employees to improve decision-making.
‘Machines are not built to understand human language, but AI has the ability to understand and generate content in human language’ sites the Scientific Reports. Indeed, since demands have shifted from strictly in-store shopping to online shopping, with e-commerce becoming a vital part of the modernising global economy, NLP combines computational linguistics with AI techniques.
“Amazon uses LLM-powered chatbots to handle and process customer inquiries”… “These chatbots can resolve 70–80% of customer service queries without human intervention,” the same report found. LLMs analyse customer behaviour through their data usage on the stores’ website. Walmart does this to allow for personalised email marketing. The clothing brand Zara uses it to predict demand for different clothing styles.
In the finance and banking world, LLMs enhance customer service by ingesting data sets to create systems to automate tasks, “such as customer queries and fraud detection, and assist in risk management.” Further research proposed that some models can overcome traditional models of banking by improving the operation and compliance in the banking system.
LMMs Restrictions: Customer Service
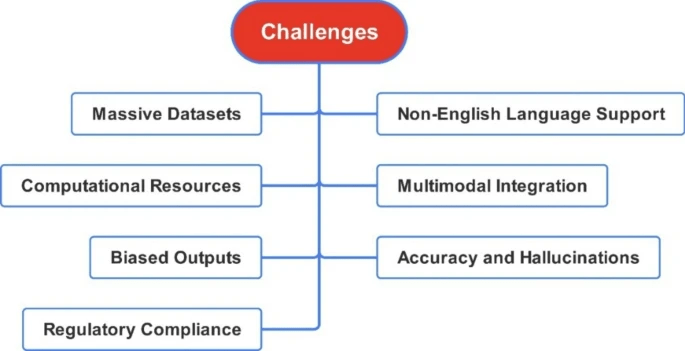
As impressive as LMMs have performed in supporting efficient in customer relations, these are language models not search engines. They are trained on massive datasets, to learn patterns in language. “The questions that arise here are: Who can use the dataset? How can the dataset be used? and when can the dataset be used,” the report asks.
Without understanding any underlying background of the data, information can be biased as datasets can consist of differing views, leading to biased outputs from LLMs. Furthermore, language models are bound to be biased because inherently language can also be biased by convention.
Data privacy also exists as an open issue; it needs personal data to cater to customer preferences. Strong data privacy needs to be in place to be able to train models without leaking client information. As ‘customer obsession’ is a leading position in most business identities, user data is being input into LLM models, creating greater concern over privacy.
Customer service is multifaceted and centred around verbal communication in a significant amount of client-facing roles. The challenge lies in LLMs’ narrow capabilities, with a primary focus on text-based inputs, which limits its scope in complex fields requiring multimodal understanding to deliver outcomes.
Future of Customer service?
LLMs are developing rapidly in traditional spaces reserved for one-to-one human interactions, in being able to complete tasks that would otherwise require multiple people to do; general queries or question and answers that AI can readily access. The growth has been outstanding to see, and its implementation in the e-commerce, banking and medical domains shows its varied application.
Nonetheless, these models still require further research and practice, as open issues still exist as they stand. For tasks that require assistance past text and through verbal communication, AI is limited. LLMs run off data that is sourced partially from personal information, providing risks to individuals if compromised. The other part of the data could also be skewed by bias as well.
So, is time up for customer service representatives? AI, LLMs and NLPs show that problem-solving is multifaceted and that there will exist a time when these systems will support stronger problem-solving situations. For now, we use these systems more as aide-de-camps than as complete replacements for people, especially in situations requiring nuanced communication and problem-solving.